 The Inspector provides several features for interacting with your MCP server:
### Server connection pane
* Allows selecting the [transport](/docs/concepts/transports) for connecting to the server
* For local servers, supports customizing the command-line arguments and environment
### Resources tab
* Lists all available resources
* Shows resource metadata (MIME types, descriptions)
* Allows resource content inspection
* Supports subscription testing
### Prompts tab
* Displays available prompt templates
* Shows prompt arguments and descriptions
* Enables prompt testing with custom arguments
* Previews generated messages
### Tools tab
* Lists available tools
* Shows tool schemas and descriptions
* Enables tool testing with custom inputs
* Displays tool execution results
### Notifications pane
* Presents all logs recorded from the server
* Shows notifications received from the server
## Best practices
### Development workflow
1. Start Development
* Launch Inspector with your server
* Verify basic connectivity
* Check capability negotiation
2. Iterative testing
* Make server changes
* Rebuild the server
* Reconnect the Inspector
* Test affected features
* Monitor messages
3. Test edge cases
* Invalid inputs
* Missing prompt arguments
* Concurrent operations
* Verify error handling and error responses
## Next steps
The Inspector provides several features for interacting with your MCP server:
### Server connection pane
* Allows selecting the [transport](/docs/concepts/transports) for connecting to the server
* For local servers, supports customizing the command-line arguments and environment
### Resources tab
* Lists all available resources
* Shows resource metadata (MIME types, descriptions)
* Allows resource content inspection
* Supports subscription testing
### Prompts tab
* Displays available prompt templates
* Shows prompt arguments and descriptions
* Enables prompt testing with custom arguments
* Previews generated messages
### Tools tab
* Lists available tools
* Shows tool schemas and descriptions
* Enables tool testing with custom inputs
* Displays tool execution results
### Notifications pane
* Presents all logs recorded from the server
* Shows notifications received from the server
## Best practices
### Development workflow
1. Start Development
* Launch Inspector with your server
* Verify basic connectivity
* Check capability negotiation
2. Iterative testing
* Make server changes
* Rebuild the server
* Reconnect the Inspector
* Test affected features
* Monitor messages
3. Test edge cases
* Invalid inputs
* Missing prompt arguments
* Concurrent operations
* Verify error handling and error responses
## Next steps
 ## How It Works
When you submit a query:
1. The client gets the list of available tools from the server
2. Your query is sent to Claude along with tool descriptions
3. Claude decides which tools (if any) to use
4. The client executes any requested tool calls through the server
5. Results are sent back to Claude
6. Claude provides a natural language response
7. The response is displayed to you
## Best practices
1. **Error Handling**
* Always wrap tool calls in try-catch blocks
* Provide meaningful error messages
* Gracefully handle connection issues
2. **Resource Management**
* Use `AsyncExitStack` for proper cleanup
* Close connections when done
* Handle server disconnections
3. **Security**
* Store API keys securely in `.env`
* Validate server responses
* Be cautious with tool permissions
## Troubleshooting
### Server Path Issues
* Double-check the path to your server script is correct
* Use the absolute path if the relative path isn't working
* For Windows users, make sure to use forward slashes (/) or escaped backslashes (\\) in the path
* Verify the server file has the correct extension (.py for Python or .js for Node.js)
Example of correct path usage:
```bash
# Relative path
uv run client.py ./server/weather.py
# Absolute path
uv run client.py /Users/username/projects/mcp-server/weather.py
# Windows path (either format works)
uv run client.py C:/projects/mcp-server/weather.py
uv run client.py C:\\projects\\mcp-server\\weather.py
```
### Response Timing
* The first response might take up to 30 seconds to return
* This is normal and happens while:
* The server initializes
* Claude processes the query
* Tools are being executed
* Subsequent responses are typically faster
* Don't interrupt the process during this initial waiting period
### Common Error Messages
If you see:
* `FileNotFoundError`: Check your server path
* `Connection refused`: Ensure the server is running and the path is correct
* `Tool execution failed`: Verify the tool's required environment variables are set
* `Timeout error`: Consider increasing the timeout in your client configuration
## How It Works
When you submit a query:
1. The client gets the list of available tools from the server
2. Your query is sent to Claude along with tool descriptions
3. Claude decides which tools (if any) to use
4. The client executes any requested tool calls through the server
5. Results are sent back to Claude
6. Claude provides a natural language response
7. The response is displayed to you
## Best practices
1. **Error Handling**
* Always wrap tool calls in try-catch blocks
* Provide meaningful error messages
* Gracefully handle connection issues
2. **Resource Management**
* Use `AsyncExitStack` for proper cleanup
* Close connections when done
* Handle server disconnections
3. **Security**
* Store API keys securely in `.env`
* Validate server responses
* Be cautious with tool permissions
## Troubleshooting
### Server Path Issues
* Double-check the path to your server script is correct
* Use the absolute path if the relative path isn't working
* For Windows users, make sure to use forward slashes (/) or escaped backslashes (\\) in the path
* Verify the server file has the correct extension (.py for Python or .js for Node.js)
Example of correct path usage:
```bash
# Relative path
uv run client.py ./server/weather.py
# Absolute path
uv run client.py /Users/username/projects/mcp-server/weather.py
# Windows path (either format works)
uv run client.py C:/projects/mcp-server/weather.py
uv run client.py C:\\projects\\mcp-server\\weather.py
```
### Response Timing
* The first response might take up to 30 seconds to return
* This is normal and happens while:
* The server initializes
* Claude processes the query
* Tools are being executed
* Subsequent responses are typically faster
* Don't interrupt the process during this initial waiting period
### Common Error Messages
If you see:
* `FileNotFoundError`: Check your server path
* `Connection refused`: Ensure the server is running and the path is correct
* `Tool execution failed`: Verify the tool's required environment variables are set
* `Timeout error`: Consider increasing the timeout in your client configuration
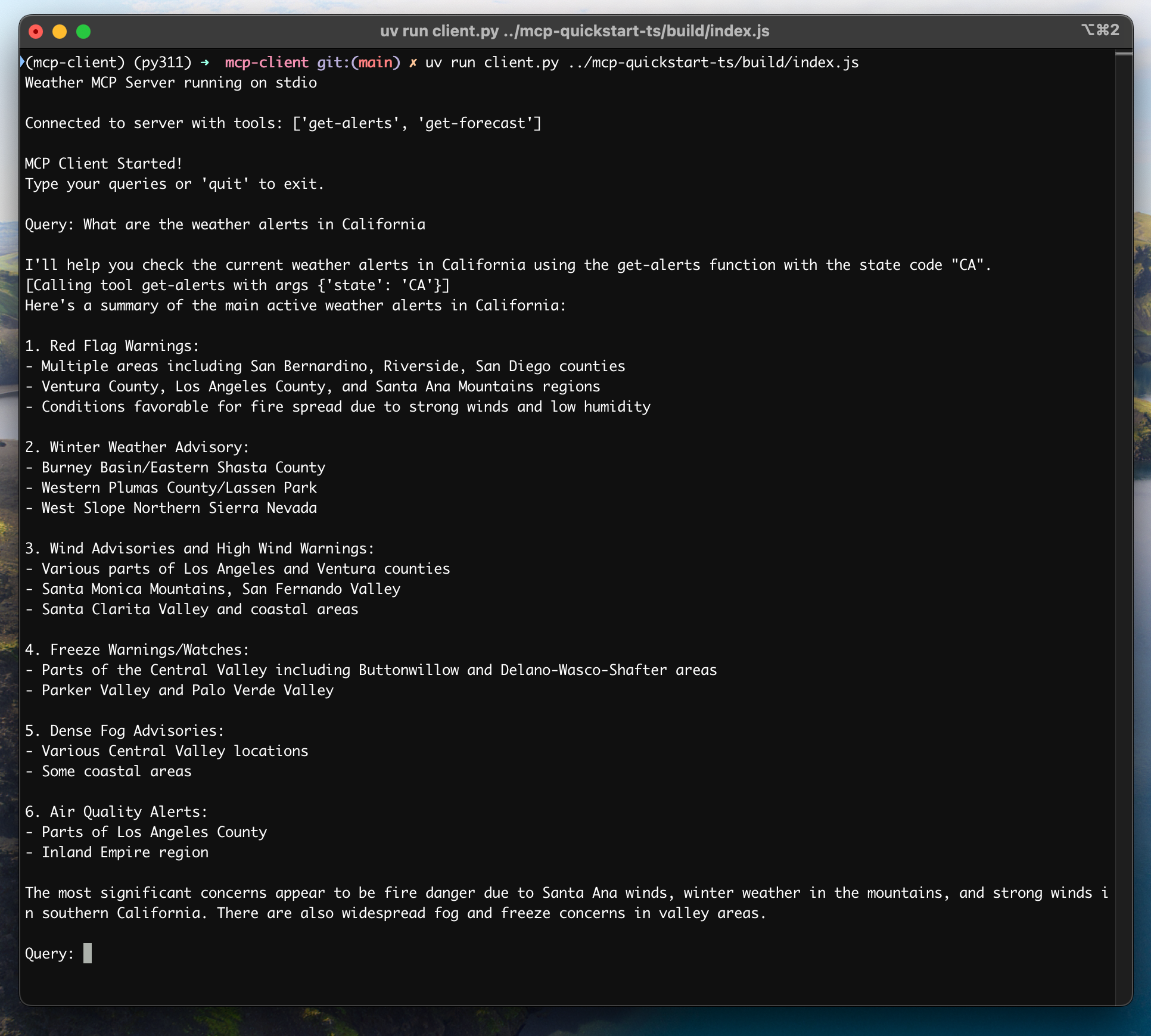
 After clicking on the hammer icon, you should see two tools listed:
After clicking on the hammer icon, you should see two tools listed:
 If your server isn't being picked up by Claude for Desktop, proceed to the [Troubleshooting](#troubleshooting) section for debugging tips.
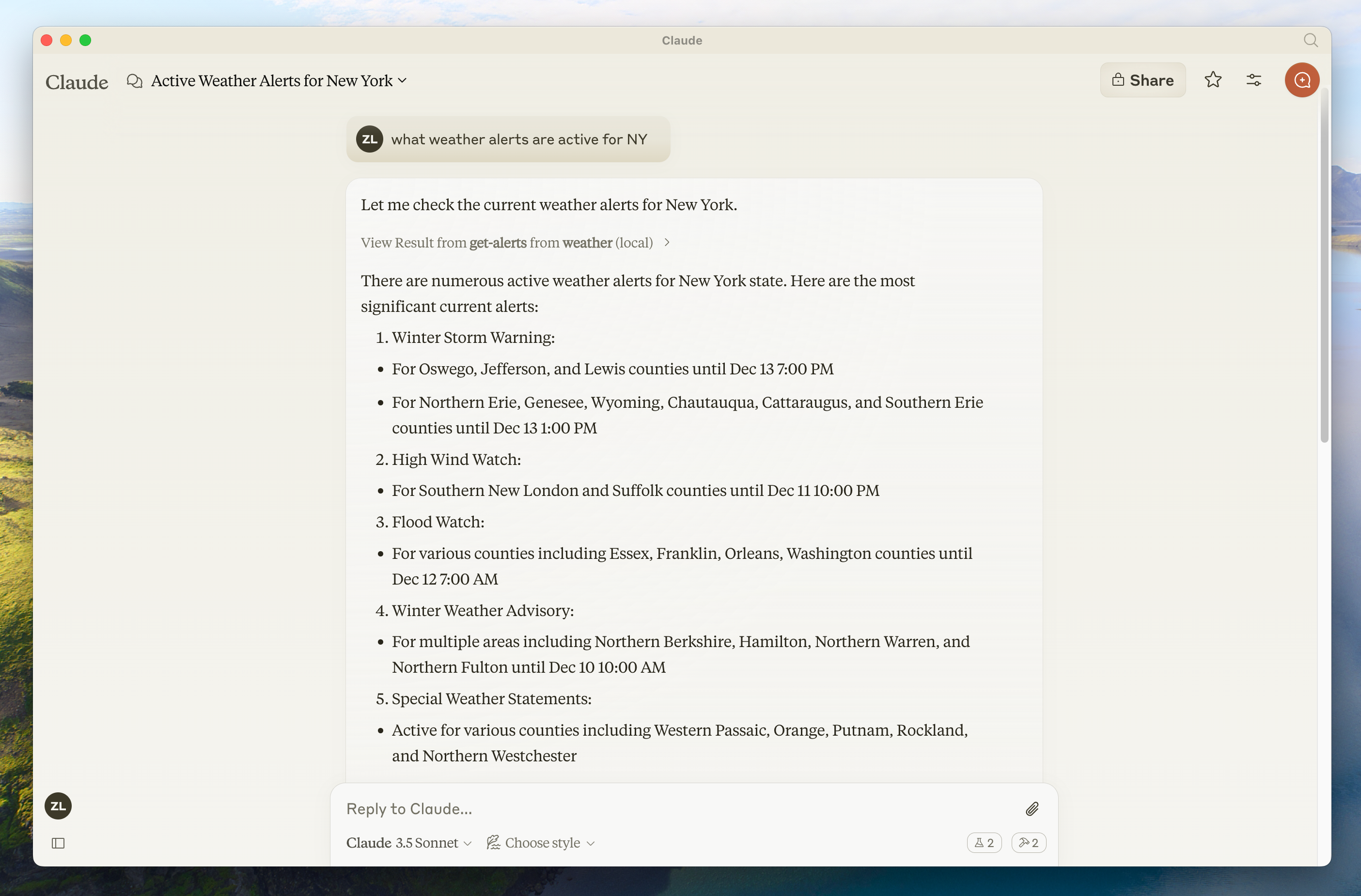
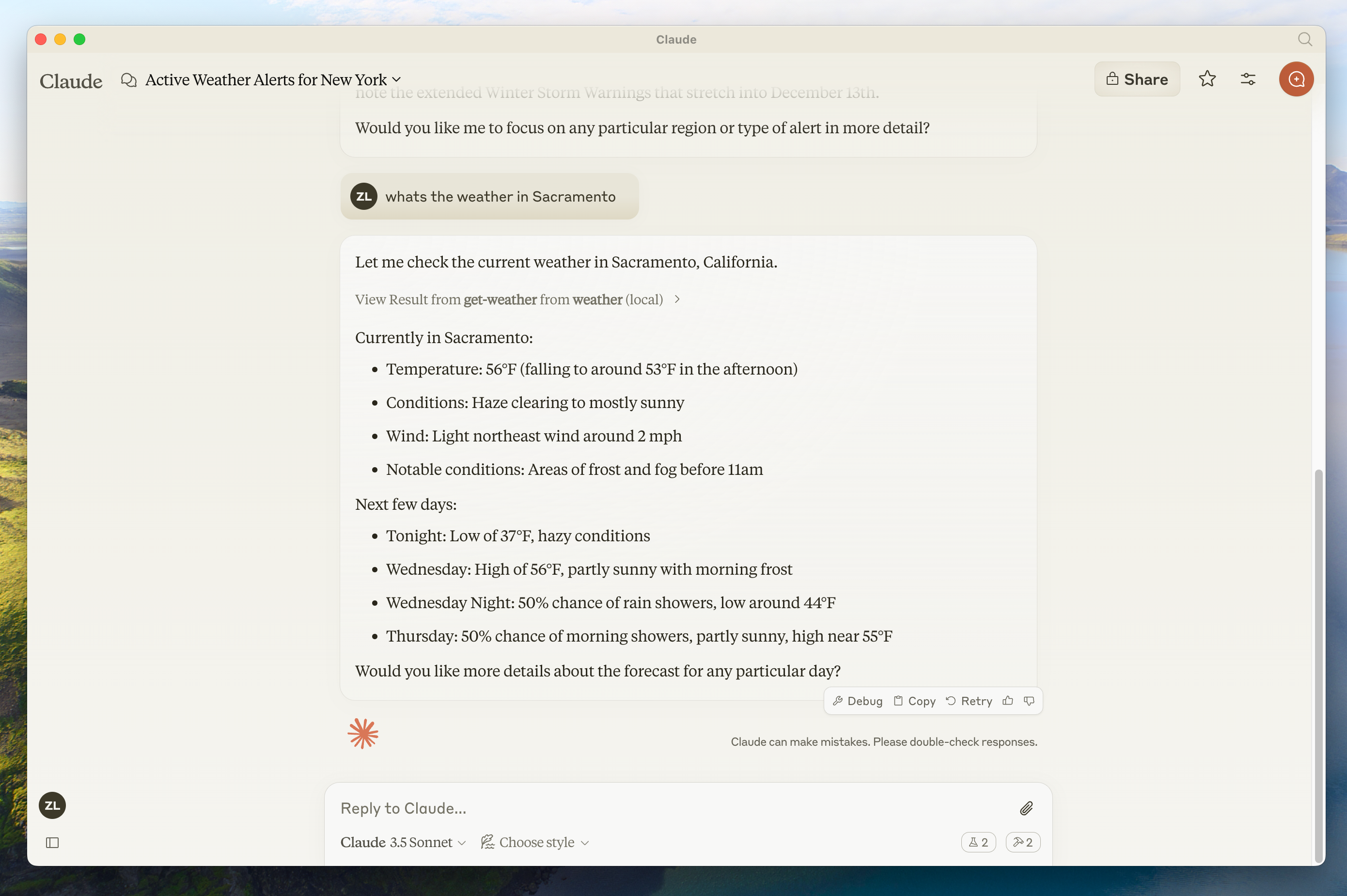
If the hammer icon has shown up, you can now test your server by running the following commands in Claude for Desktop:
* What's the weather in Sacramento?
* What are the active weather alerts in Texas?
If your server isn't being picked up by Claude for Desktop, proceed to the [Troubleshooting](#troubleshooting) section for debugging tips.
If the hammer icon has shown up, you can now test your server by running the following commands in Claude for Desktop:
* What's the weather in Sacramento?
* What are the active weather alerts in Texas?


 Don't worry — it will ask you for your permission before executing these actions!
## 1. Download Claude for Desktop
Start by downloading [Claude for Desktop](https://claude.ai/download), choosing either macOS or Windows. (Linux is not yet supported for Claude for Desktop.)
Follow the installation instructions.
If you already have Claude for Desktop, make sure it's on the latest version by clicking on the Claude menu on your computer and selecting "Check for Updates..."
Don't worry — it will ask you for your permission before executing these actions!
## 1. Download Claude for Desktop
Start by downloading [Claude for Desktop](https://claude.ai/download), choosing either macOS or Windows. (Linux is not yet supported for Claude for Desktop.)
Follow the installation instructions.
If you already have Claude for Desktop, make sure it's on the latest version by clicking on the Claude menu on your computer and selecting "Check for Updates..."
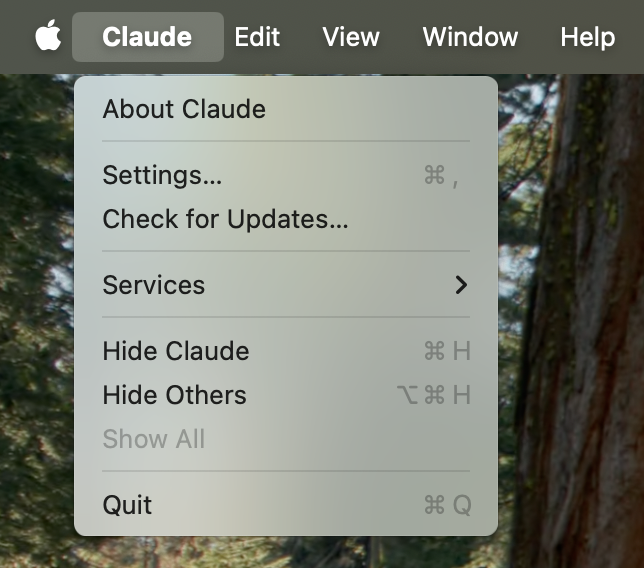 Click on "Developer" in the lefthand bar of the Settings pane, and then click on "Edit Config":
Click on "Developer" in the lefthand bar of the Settings pane, and then click on "Edit Config":
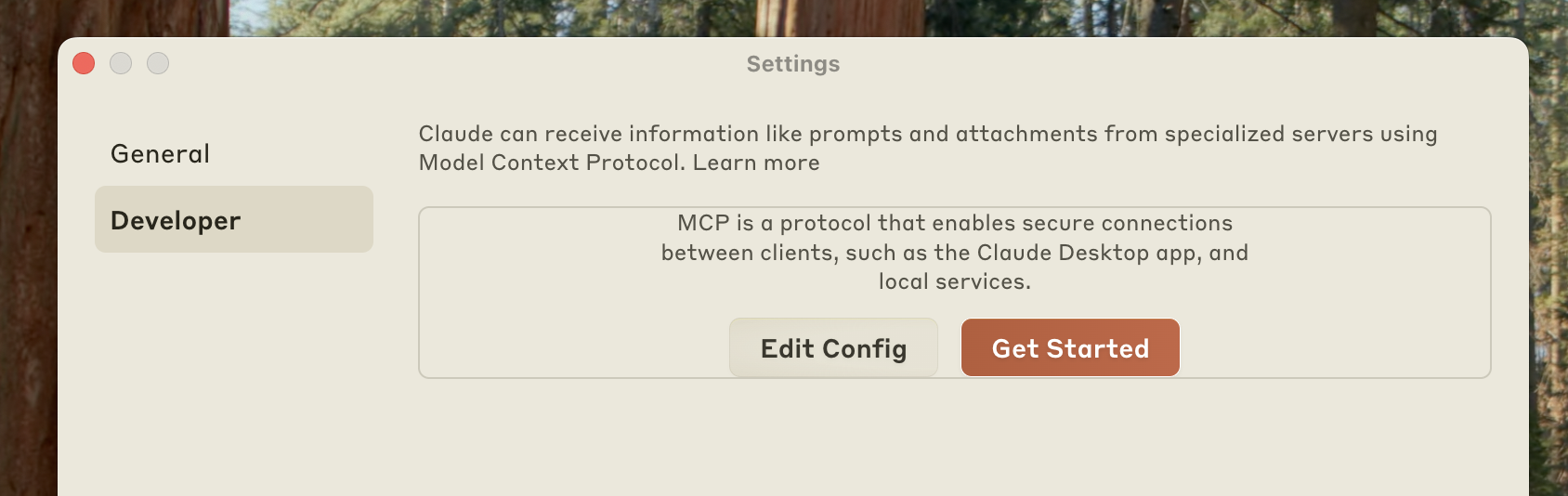 This will create a configuration file at:
* macOS: `~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json`
* Windows: `%APPDATA%\Claude\claude_desktop_config.json`
if you don't already have one, and will display the file in your file system.
Open up the configuration file in any text editor. Replace the file contents with this:
This will create a configuration file at:
* macOS: `~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json`
* Windows: `%APPDATA%\Claude\claude_desktop_config.json`
if you don't already have one, and will display the file in your file system.
Open up the configuration file in any text editor. Replace the file contents with this:
 After clicking on the hammer icon, you should see the tools that come with the Filesystem MCP Server:
After clicking on the hammer icon, you should see the tools that come with the Filesystem MCP Server:
 If your server isn't being picked up by Claude for Desktop, proceed to the [Troubleshooting](#troubleshooting) section for debugging tips.
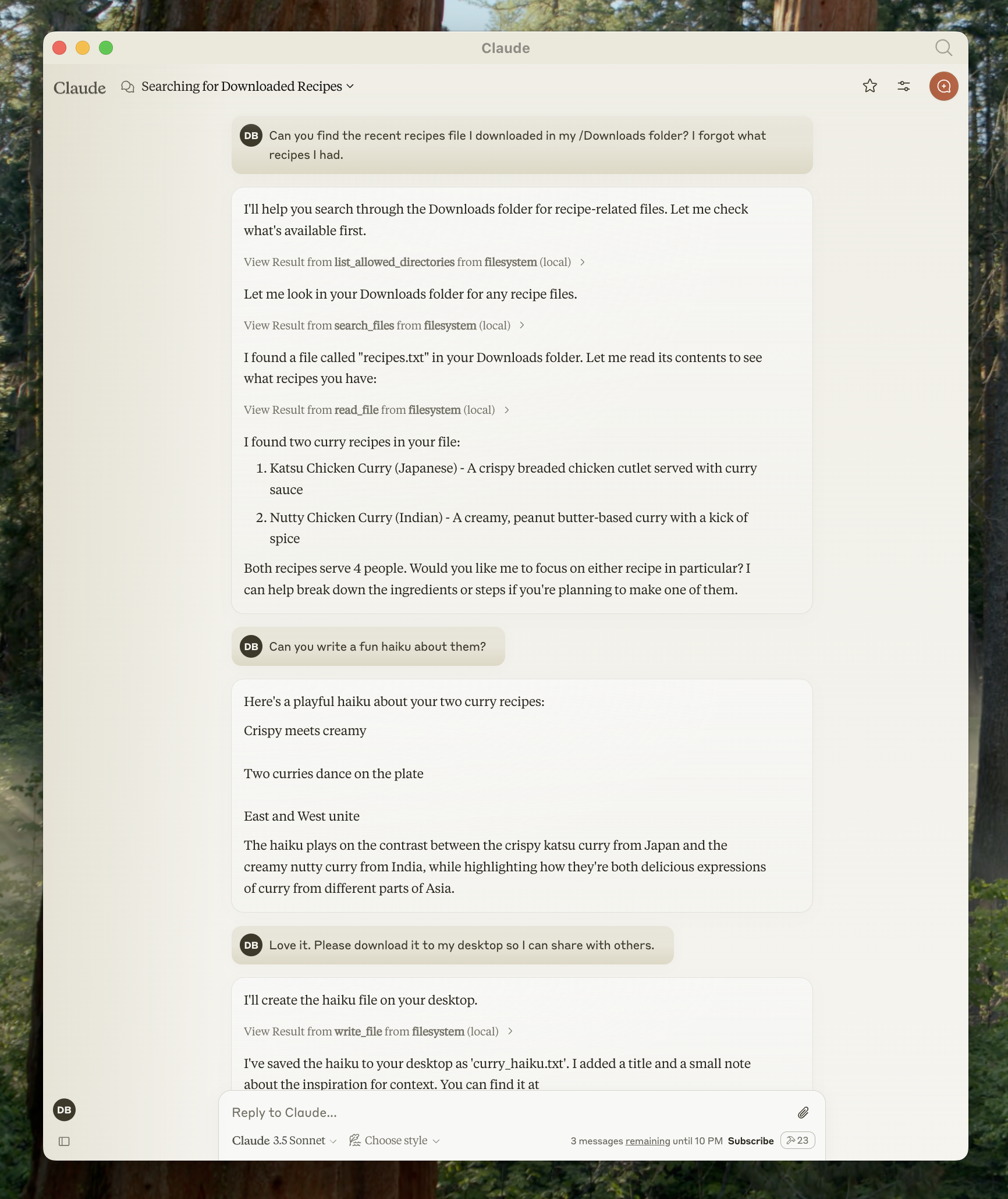
## 4. Try it out!
You can now talk to Claude and ask it about your filesystem. It should know when to call the relevant tools.
Things you might try asking Claude:
* Can you write a poem and save it to my desktop?
* What are some work-related files in my downloads folder?
* Can you take all the images on my desktop and move them to a new folder called "Images"?
As needed, Claude will call the relevant tools and seek your approval before taking an action:
If your server isn't being picked up by Claude for Desktop, proceed to the [Troubleshooting](#troubleshooting) section for debugging tips.
## 4. Try it out!
You can now talk to Claude and ask it about your filesystem. It should know when to call the relevant tools.
Things you might try asking Claude:
* Can you write a poem and save it to my desktop?
* What are some work-related files in my downloads folder?
* Can you take all the images on my desktop and move them to a new folder called "Images"?
As needed, Claude will call the relevant tools and seek your approval before taking an action:
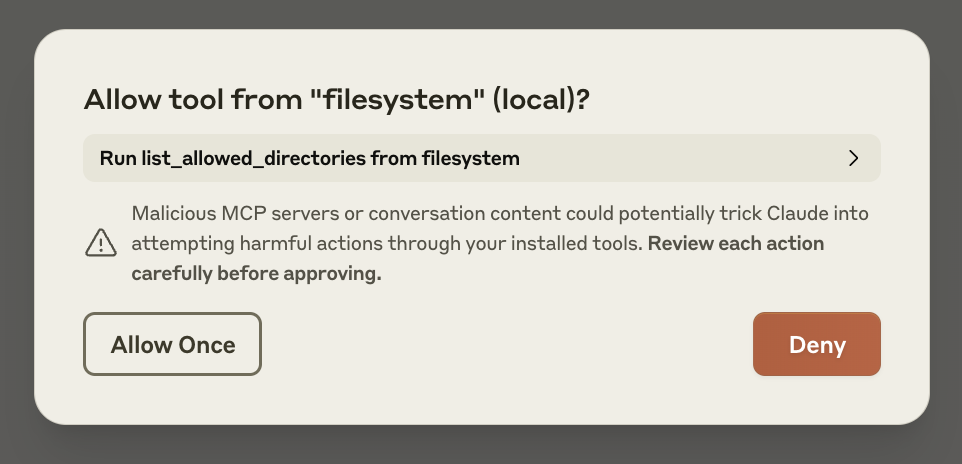 ## Troubleshooting
## Troubleshooting
- Bidirectional communication through stdin/stdout
- Process-based integration support
- Simple setup and configuration
- Lightweight implementation
Creates WebFlux-based SSE server transport.
Requires the mcp-spring-webflux dependency.
Implements the MCP HTTP with SSE transport specification, providing:
- Reactive HTTP streaming with WebFlux
- Concurrent client connections through SSE endpoints
- Message routing and session management
- Graceful shutdown capabilities
Creates WebMvc-based SSE server transport.
Requires the mcp-spring-webmvc dependency.
Implements the MCP HTTP with SSE transport specification, providing:
- Server-side event streaming
- Integration with Spring WebMVC
- Support for traditional web applications
- Synchronous operation handling
Creates a Servlet-based SSE server transport. It is included in the core mcp module.
The HttpServletSseServerTransport can be used with any Servlet container.
To use it with a Spring Web application, you can register it as a Servlet bean:
Implements the MCP HTTP with SSE transport specification using the traditional Servlet API, providing:
- Asynchronous message handling using Servlet 6.0 async support
- Session management for multiple client connections
-
Two types of endpoints:
- SSE endpoint (
/sse) for server-to-client events - Message endpoint (configurable) for client-to-server requests
- SSE endpoint (
- Error handling and response formatting
- Graceful shutdown support